Highlights
- •
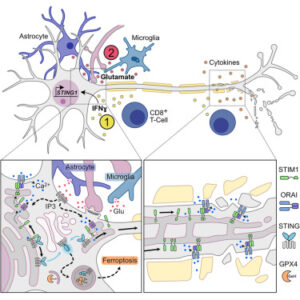
STING is expressed in human and mouse neurons solely under inflammatory conditions
- •
Excitotoxicity activates a non-canonical STIM1-STING signaling pathway in neurons
- •
Neuronal STING activation leads to autophagic GPX4 degradation and ferroptosis
- •
Targeting neuronal STING protects from inflammation-induced neurodegeneration
Summary
Inflammation-induced neurodegeneration is a defining feature of multiple sclerosis (MS), yet the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. By dissecting the neuronal inflammatory stress response, we discovered that neurons in MS and its mouse model induce the stimulator of interferon genes (STING). However, activation of neuronal STING requires its detachment from the stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1), a process triggered by glutamate excitotoxicity. This detachment initiates non-canonical STING signaling, which leads to autophagic degradation of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), essential for neuronal redox homeostasis and thereby inducing ferroptosis. Both genetic and pharmacological interventions that target STING in neurons protect against inflammation-induced neurodegeneration. Our findings position STING as a central regulator of the detrimental neuronal inflammatory stress response, integrating inflammation with glutamate signaling to cause neuronal cell death, and present it as a tractable target for treating neurodegeneration in MS.
.
Woo MS, Mayer C, Binkle-Ladisch L, Sonner JK, Rosenkranz SC, Shaposhnykov A, Rothammer N, Tsvilovskyy V, Lorenz SM, Raich L, Bal LC, Vieira V, Wagner I, Bauer S, Glatzel M, Conrad M, Merkler D, Freichel M, Friese MA. STING orchestrates the neuronal inflammatory stress response in multiple sclerosis. Cell. 2024 Jun 7:S0092-8674(24)00576-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.05.031. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38878778.