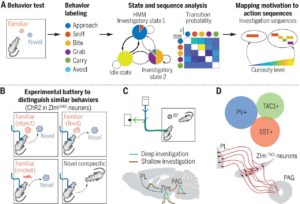
 “Curiosity is what drives organisms to investigate each other and their environment. It is considered by many to be as intrinsic as hunger and thirst, but the neurobiological mechanisms behind curiosity have remained elusive. In mice, Ahmadlou et al. found that a specific population of genetically identified γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)—ergic neurons in a brain region called the zona incerta receive excitatory input in the form of novelty and/or arousal information from the prelimbic cortex, and these neurons send inhibitory projections to the periaqueductal gray region. This circuitry is necessary for the exploration of new objects and conspecifics.”
“Curiosity is what drives organisms to investigate each other and their environment. It is considered by many to be as intrinsic as hunger and thirst, but the neurobiological mechanisms behind curiosity have remained elusive. In mice, Ahmadlou et al. found that a specific population of genetically identified γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)—ergic neurons in a brain region called the zona incerta receive excitatory input in the form of novelty and/or arousal information from the prelimbic cortex, and these neurons send inhibitory projections to the periaqueductal gray region. This circuitry is necessary for the exploration of new objects and conspecifics.”
Ahmadlou M, Houba JHW, van Vierbergen JFM, Giannouli M, Gimenez GA, van Weeghel C, Darbanfouladi M, Shirazi MY, Dziubek J, Kacem M, de Winter F, Heimel JA. A cell type-specific cortico-subcortical brain circuit for investigatory and novelty-seeking behavior. Science. 2021 May 14;372(6543):eabe9681.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33986154/
